1. entrySet() + Iterator
Map은 Collection 인터페이스를 상속하지 않았기 때문에 Iterator를 갖지 않습니다.
따라서 entrySet() 메서드 호출을 통해 Collection 인터페이스를 상속한 Set을 리턴한 후 Iterator로 순회하면 됩니다.
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "1번째 값");
map.put(2, "2번째 값");
Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> it = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = it.next();
System.out.println("Key: " + entry.getKey());
System.out.println("Value: " + entry.getValue());
}Key: 1
Value: 1번째 값
Key: 2
Value: 2번째 값
2. entrySet() + for each
Set은 향상된 for문으로도 순회할 수 있습니다. Iterator로 순회하는 것 보다 코드가 간단합니다.
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "1번째 값");
map.put(2, "2번째 값");
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("Key: " + entry.getKey());
System.out.println("Value: " + entry.getValue());
}Key: 1
Value: 1번째 값
Key: 2
Value: 2번째 값
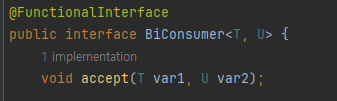
3. forEach(Biconsumer<K, V> action)
Map은 forEach 메서드로 순회할 수 있습니다.
Map을 순회하며 수행할 로직은 Biconsumer<K, V> 람다식을 통해 지정합니다.
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "1번째 값");
map.put(2, "2번째 값");
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("Key: " + key);
System.out.println("Value: " + value);
});Key: 1
Value: 1번째 값
Key: 2
Value: 2번째 값
위 forEach(Biconsumer<K, V> action) 메서드는 다음의 코드를 수행한 것과 동일합니다.
BiConsumer<Integer, String> action = (key, value) -> {
System.out.println("Key: " + key);
System.out.println("Value: " + value);
};
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
action.accept(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
Reference
'개발 > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 익명 클래스, 익명 객체란? (0) | 2024.06.18 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 자바 배열 원소를 이어 붙여서 출력하는 4가지 방법 (0) | 2024.05.31 |
| [Java] 자바 Optional 올바른 사용법 (0) | 2024.05.23 |
| [Java] 자바 String 문자열, char 문자를 int 정수로 변환하기 (0) | 2024.05.21 |
| [Java] 자바 객체 배열, 리스트 정렬하기 - Comparable vs. Comparator (0) | 2024.05.19 |